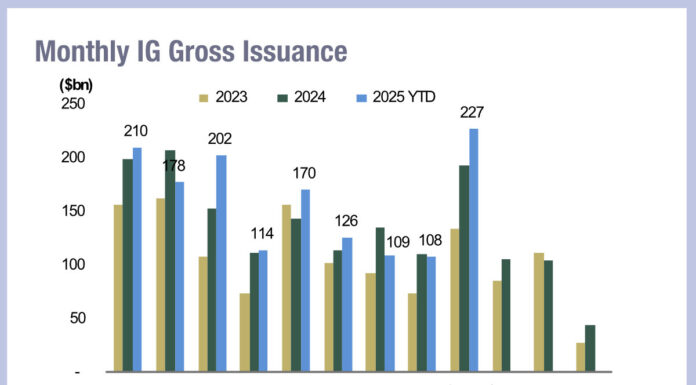
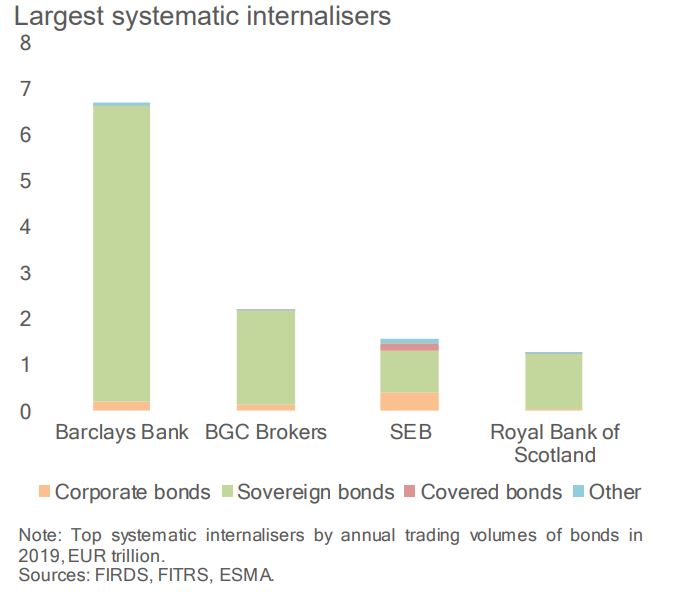
The European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) has republished its ESMA Annual Statistical Report, now stating that the largest systematic internalisers (SIs) for bond trading volume in 2019 were Barclays (€6.7 trillion), BNP Paribas (€2.2 trillion), SEB (€1.6 trillion) and Royal Bank of Scotland (€1.2 trillion).
The report is an analysis of trading activity in equity and non-equity instruments in Europe. It found significant fragmentation of trading for most bonds across trading venues and systematic internalisers (SIs); using the Herfindahl–Hirschman Index (HHI) as a proxy for market concentration, on a scale where ‘0’ is concentrated and ‘1’ is fragmented, corporate and government bonds measured 0.94, ‘other’ types, such as convertible bonds, measured 0.95 and covered bonds measured 0.88; covered bonds are typically a feature of specific geographical markets.
Over-the-counter trading accounted for €50.4 trillion of bond trading by volume, the 102 SIs in the European Economic Area (EEA) accounted for €26.1 trillion of traded volume, the 94 multilateral trading facilities (MTFs) for approximately 15% and the 30 organised trading facilities (OTFs) for closer to 10%.
When originally published, ESMA had mistakenly included interdealer broker BGC, which runs an OTF, as an SI, putting it in second place behind Barclays, a place now taken by BNP Paribas.
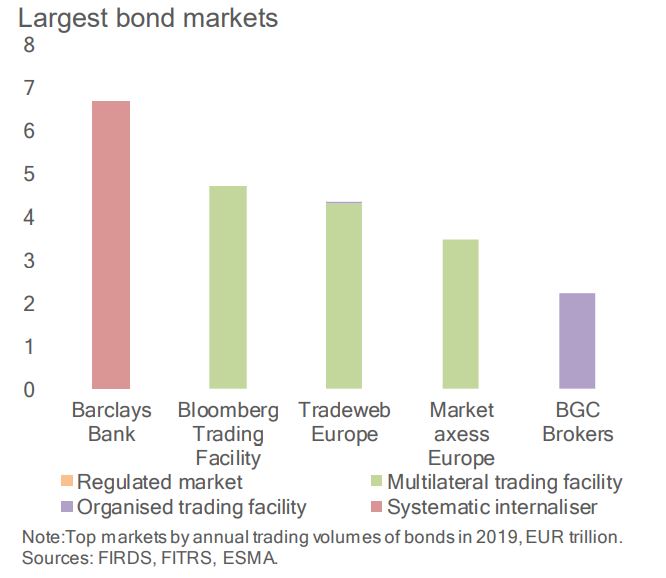
With nearly €6.7 trillion traded in 2019, Barclays SI was Europe’s biggest venue followed by Bloomberg Trading Facility, Tradeweb, MarketAxess and BGC’s OTF. BNP Paribas’s SI traded closer to €2 trillion over the year.
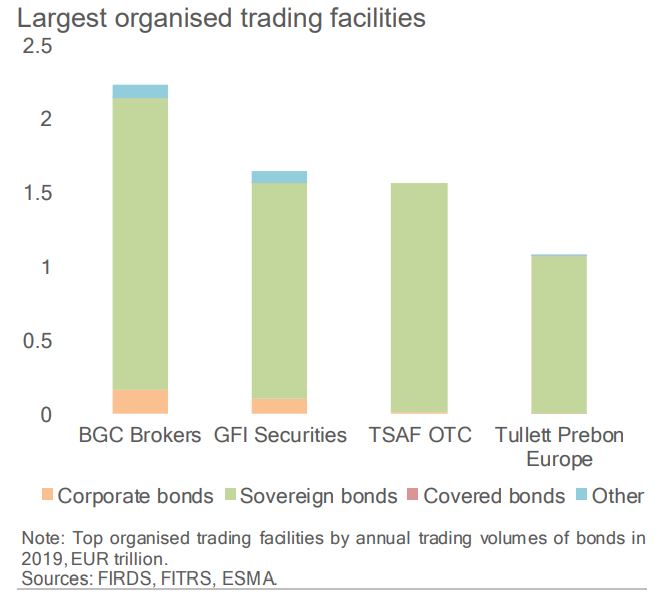
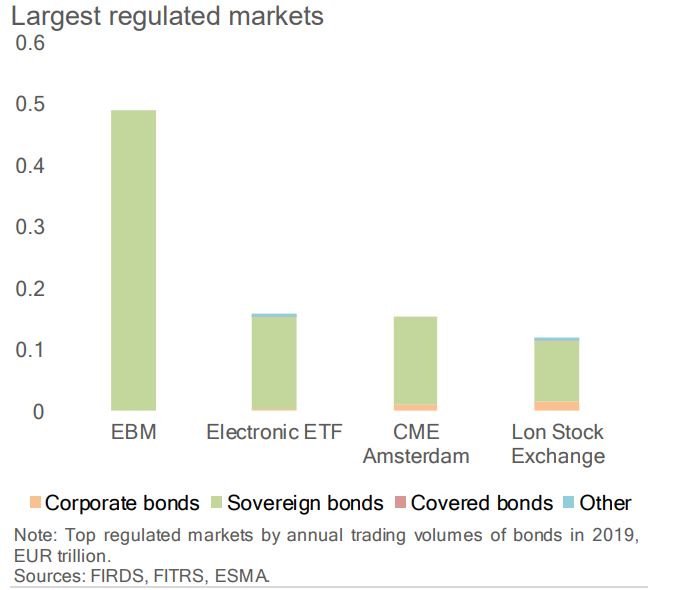
BGC was the largest OTF, while MTS’s EBM ran the largest regulated market and the fourth largest MTF.
©Markets Media Europe 2025